
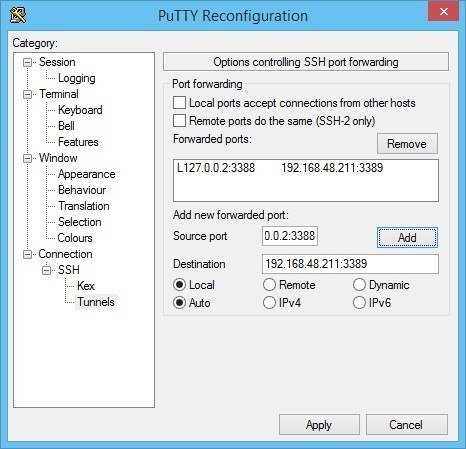
Once the VNC connection is terminated logout or exit from the ssh session and the ssh tunnel is closed. The port number will follow the display indicated (5900+display).Ī normal VNC connection should be established to the remote system. Just change it to a ":1" to use 5901 as indicated in the second ssh example. Ssh -L 5901:127.0.0.2:5900 this connection is established you can switch to another terminal and startup the vncviewer with the following command: The command to setup the local port 5901 to route to 5900 on the remote system would look like this: For example, when vncviewer is run for display :1 it will attempt to connect to port 5901 rather than 5900 (vncviewer host:1). If port 5900 is already in use on the administrator system a different port could be used. Ssh -L 5900:127.0.0.2:5900 -L port:host:port specifies that the given port on the local administrator host is to be forwarded to the given host and port on the remote side. From a terminal run the following command: On the administrator system a ssh connection will need to be established to the remote system. Add ssh to the allowed services if needed. Verify your firewall settings in YaST->Security and Users->Firewall. By default the firewall is turned on and ssh is blocked.
The client systems must also allow an ssh connection as we will use a ssh tunnel to secure the VNC communication. The Remote Desktop selection in the Control Center runs "vino" which is a vncserver equivalent that allows the connection to display :0 (what the user is viewing) on port 5900. It starts a session independent from the users so you do not see the users desktop. There is also another selection for Remote Administration in YaST but it does not allow a connection to display :0. The reason that we do this is so we can piggyback off the RSA security provided by the SSH connection, which we cannot easily recreate natively using a VNC client.
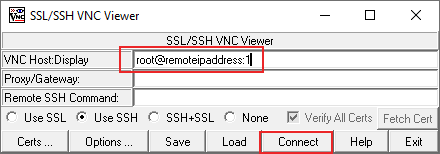
When you’re ready, click the Connect button.Remote systems must have the Remote Desktop feature enabled. Open the Control Center and under the System group take the selection for Remote Desktop. VNC traffic by default uses port 5901, so this configuration will take any VNC connection from localhost:1 (on your local system) and route it through SSH to your remote system. For example, Make sure you select the Use SSH or SSL+SSL option before you connect. Under VNC Host:Display, type Replace SSHusername with the username you’d use for your SSH connection, and replace remoteIPaddress with your remote desktop IP address. Open the SSVNC client and, within the main SSVNC client window, fill in the required fields.A practical use of SSH tunneling with local and remote port forwarding would be to securely exchange the desktops between two PCs using the VNC protocol.

#VNC THROUGH SSH PC#
SSVNC is supported by Windows and Linux operating systems. In other words, using VNC with SSH port forwarding makes a port from one PC appear on another PC through a SSH connection, providing a secure path for the VNC traffic. One example is SSVNC which, while basic, will tunnel over SSH before making a VNC connection. Other VNC clients, however, do include SSH tunneling within the client itself. While TightVNC is a popular Windows client for VNC connections, it doesn’t support SSH tunneling within the client itself, requiring you to use PuTTY to make the connection.
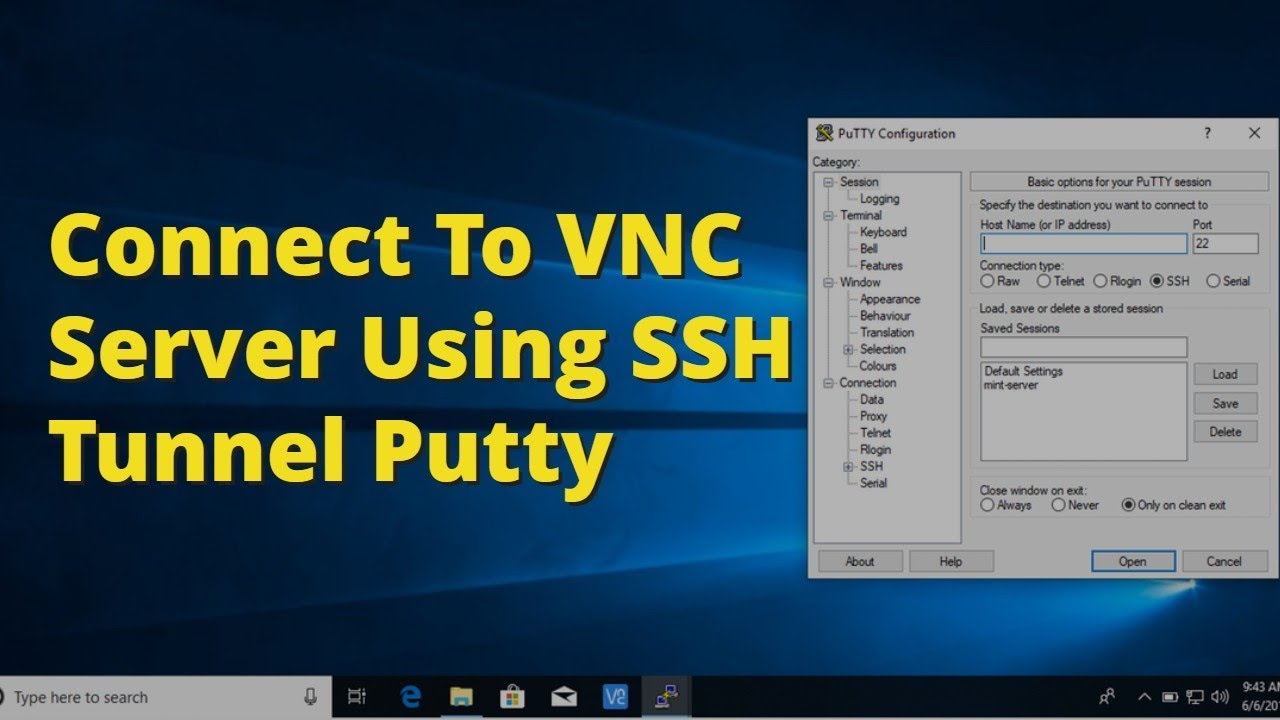
If your SSH connection is working correctly, TightVNC should load your remote VNC desktop window, ready for you to use.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
